What is Rebranding? Explaining the Process and Timing for Success
- カテゴリ:
Due to changes in market conditions and the rise of competitors, brands that once shone brightly may lose their appeal over time. “Rebranding” is an effective means for companies to overcome such situations and get back on a growth trajectory. However, it’s not simply a matter of changing the logo – without following a strategic process, there’s also the risk of losing existing fans.
This article provides detailed explanations of the correct meaning and purpose of rebranding, implementation timing, and specific steps to lead to success, incorporating actual corporate case studies.
What is Rebranding? Differences from New Branding
Rebranding refers to activities that reconstruct the brand that a company or its products and services have built up over time, adding new value. When operating a business for a long time, it’s not uncommon for founding principles and product appeal to become misaligned with the needs of the times and customer values. Rebranding is a management strategy to correct such misalignments and “regenerate” or “evolve” the brand to match the changed environment.
【Related Article】What is PR? A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners from Job Content to Strategy Development! | Column | SUNNY SIDE UP Inc.
Reviewing existing brand assets and reconstructing new value
The most important point in rebranding is not to deny everything from the past, but to leverage existing assets. The task requires selecting “strengths that should not be changed” such as history, technological capabilities, customer trust, and brand recognition, and “elements that should be changed” to match the times. For example, this applies when a long-established company maintains traditional techniques while updating its design to a contemporary style to appeal to younger generations. The essence of rebranding is the process of restoring brand brilliance through refinement rather than scrapping and rebuilding.
Differences from new branding created from scratch
While they share the word “branding,” new branding launched from scratch and rebranding differ in their prerequisites and approaches.
The following table organizes the main differences between the two.
| Item | New Branding | Rebranding |
|---|---|---|
| Target | New company New business New product |
Existing company Existing business Existing product |
| Existing assets | None | Yes (history, recognition, customers, employees) |
| Main challenges | Recognition acquisition Trust building |
Image renewal New customer acquisition Regaining novelty Eliminating negative image |
| Difficulty | Concepts can be designed freely | Difficult due to the need to resolve gaps with existing image |
| Risk | Risk of not being recognized Risk of difficulty in differentiation |
Risk of existing customer defection Risk of generating resistance from existing employees |
Rebranding involves changing already established images, which may provoke resistance from both internal and external stakeholders. More delicate consensus building and stronger commitment to change are required compared to new branding.
Three Purposes for Companies to Undertake Rebranding

Why is it necessary to undertake rebranding despite the risks? The purpose is not merely cosmetic changes, but solving management challenges. The main purposes and benefits that companies gain from rebranding can be broadly classified into three categories.
Resolving misalignment with changing times and target demographics
Consumer lifestyles and values are constantly changing. While “cheap and mass-produced items” may have been sought after in the past, “sustainable and high-quality items” might be preferred today. By conducting rebranding, companies can tune their brand approach to match such changes in the times. For brands experiencing aging target demographics, incorporating concepts, designs, creative elements, and UI/UX that resonate with younger generations can rejuvenate the customer base and ensure brand continuity. Enhancing market adaptability is an essential condition for business continuity.
Differentiating from competitors and establishing market superiority
When similar products or services increase in the market, companies become easily caught up in price competition. By redefining unique value propositions through rebranding and establishing clear differences from competitors, companies can be chosen for factors other than price. If “brand-specific purchases” increase where customers buy “because it’s this brand,” there’s no need for discounting, leading to improved profit margins. To achieve this, companies must clarify where their brand strengths lie and deeply understand what expectations and benefits actual purchasers and users feel. Furthermore, by clearly deciding what the brand will “do” and “not do,” brand consistency and uniqueness can be maintained. Making buried brand personalities stand out and re-establishing market positioning creates competitive advantages.
Internal awareness reform and organizational revitalization and recruitment enhancement
The effects of rebranding are not limited to external impacts. Rather, the internal impact (inner branding effect) can be said to be very significant. Through the process of redefining brand principles and vision, employees can re-recognize their company’s strengths and direction, improving organizational unity and employee motivation. Additionally, being reborn as an attractive brand becomes a powerful weapon in recruitment activities. Being recognized as a “company actively contributing to society,” “a company that has worked for years to maintain high credibility,” or “a company with a solid vision” makes it easier to attract talented individuals, ultimately boosting the company’s growth potential.
Timing to Consider Rebranding

Rebranding is not something that can be done whenever you feel like it. To succeed, it’s necessary to identify the appropriate timing when internal and external momentum is building. Generally, here are three timing indicators that signal when rebranding should be considered.
Organizational milestones such as company anniversaries or management structure changes
Timing such as 10th, 50th, or 100th anniversaries, presidential succession due to business succession, or organizational restructuring due to M&A (mergers and acquisitions) provides excellent opportunities for rebranding. These occasions naturally attract attention from internal and external stakeholders, making it easier to gain acceptance for change. By declaring brand renewal with messages like “transforming for the next 100 years” or “challenging new markets under new management,” companies can strongly impress stakeholders with their evolution.
During growth stagnation such as declining sales or shrinking market share
When clear negative signs are visible, it’s also an organizational milestone like anniversaries or management changes. When sales have been flat or declining over an extended period, this may indicate declining brand power rather than product issues. When perceived as “outdated,” “boring,” or “unclear about what they provide,” superficial promotional measures won’t lead to recovery. Fundamental reform through rebranding is necessary to give the market an impact of being “evolved” or “diversified.”
When expanding business domains or making major target demographic changes
As companies grow, their initial business content may no longer match current reality. For example, a company that once dealt with specific products may have evolved into a comprehensive solution provider. In such cases, maintaining the previous brand name or logo fails to properly communicate the value they can provide. By conducting rebranding when targets or provided value change significantly – such as business domain expansion, overseas expansion, or shifting from B2B to B2C – companies can build brand images that match their new business reality.
To succeed in rebranding, meticulous strategic design is essential. SUNNY SIDE UP’s strategic planning provides total support from branding strategy formulation to integrated marketing communication construction. With accurate analysis based on market research and expertise cultivated from extensive experience, we realize brand value reconstruction. Please see below for details on strategic planning.
Strategic Planning | Services | PR Company | SUNNY SIDE UP Inc.
Five Steps for Successful Rebranding
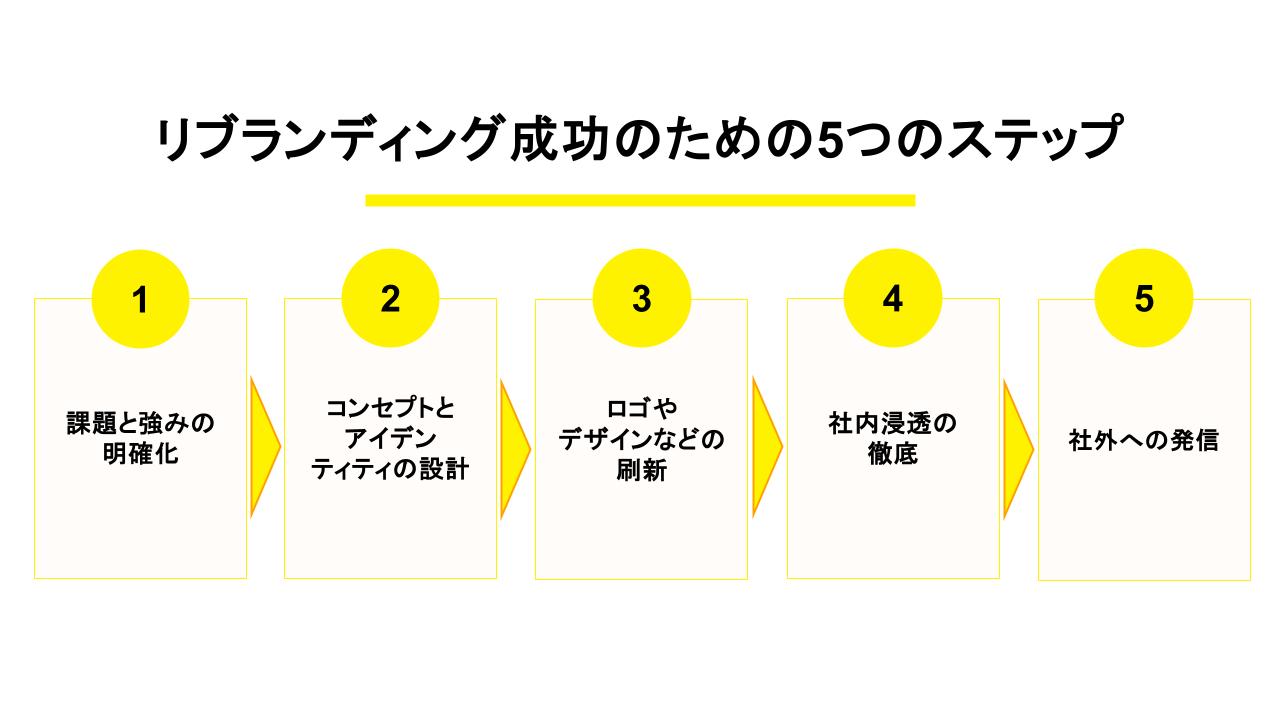
Rebranding doesn’t end with changing the logo. It’s important to follow a consistent process from research to concept design, creative development, and penetration activities. Here we explain the five foundational steps.
Step 1: Clarify brand challenges and strengths through current situation analysis
The first step is to objectively understand how your brand is currently perceived. Conduct interviews and surveys with management, employees, existing customers, business partners, and the general public who are unfamiliar with the brand. This reveals gaps between “strengths the company thinks it has” and “appeal customers feel,” as well as the real challenges the brand faces. Accurate current situation analysis (As-Is) becomes the foundation for envisioning the desired state (To-Be).
Step 2: Design new concepts that leverage existing assets
Based on analysis results, redefine the core brand concept (brand identity). Articulate “to whom,” “what value,” and “how to provide it,” establishing mission, vision, values, etc. Here, it’s important to incorporate “authenticity” rooted in the company’s history and DNA, not just following trends. This concept becomes the judgment criterion for all subsequent design development, PR activities, employee behavioral guidelines, and product/service marketing activities.
Step 3: Reconstruct logo, design, and brand identity
Transform the established concept into visible form (visual identity). Refresh brand logos, brand colors, taglines (catchphrases), package design, websites, and advertising creative design. When doing so, clearly organize “to whom and in what context to deliver.”
① For existing customers: Redefine past value in “today’s language”
For customers who have long used that brand or product, rebranding risks making them feel “the beloved brand has become distant.” While preserving the goodness and context of the past, it’s necessary to re-articulate “why it should still be chosen today” using contemporary values.
・Respect the feelings and historical background embedded in brand logos and colors
・Update within a range that doesn’t compromise the “authenticity” that past customers felt
・Carefully determine what should be changed and what should be preserved
② For new customers: Value design that communicates without knowing the past
On the other hand, for customer segments of generations or preferences that previously had no contact, it’s necessary to communicate the value, background, and usage of products and brands in an accessible way so they can understand “why this continues to be chosen today as it was in the past” even without knowing the historical context of past products and brands.
Examples)
・Express “why this brand is needed now” intuitively through package design, websites, advertising creative, etc.
・Present contexts that fit contemporary lifestyle scenes and values through catchphrases
・In some cases, consider changing product/service naming to refresh brand positioning
Step 4: Ensure thorough internal penetration through inner branding
Before announcing the new brand, conducting internal penetration (inner branding) is extremely important. Top management must personally explain to employees why rebranding is being conducted and what feelings are embedded in the new brand, gaining their empathy. If employees don’t understand and develop attachment to the new brand, they cannot deliver that value to customers. Through distributing brand books and conducting workshops, all employees are developed into “brand embodiers.”
Step 5: Communicate externally through outer branding
Once the internal structure is in place, it’s time to unveil the new brand externally (outer branding). Distribute press releases, hold press conferences, launch new websites, deploy campaigns, and officially launch the brand. Subsequently, gradually introduce products and services reflecting the rebranding to the market, providing new brand experiences to customers. Rather than simply communicating “the logo has changed,” communicate the underlying “corporate will” and “promises for the future” as a story. Don’t end with one-time buzz creation, but establish the new brand image in the market through continuous communication.
Precautions to Avoid Rebranding Failures
While rebranding is a powerful tool, incorrect implementation can cause significant damage. Finally, we’ll explain points that require particular attention to avoid failure.
Don’t leave existing customers behind – communicate the intent of change
The biggest risk is losing existing fans (loyal customers). Comments like “I preferred the previous design” or “I’m sad it changed” will inevitably arise. While trying to acquire new customers, don’t neglect those who have supported you. Communication that sincerely and carefully explains why change was necessary and what benefits the change brings to customers is essential. Communication methods shouldn’t be uniform either – it’s important to combine various channels such as press releases, company-operated social media (SNS), and collaboration with influential influencers and KOLs (Key Opinion Leaders) depending on the situation.
Review essential value, not superficial design changes
Making only the design stylish while leaving the content (products, services, employee awareness) unchanged will cause rebranding to fail. Customers will quickly see through “it’s just appearance.” Rebranding is an activity that questions the company’s very existence. It requires enhancing the organization’s overall transformation capability, including customer experience redesign, product/service quality improvement and functional enhancement, employee awareness reform and skill development, and strengthening responsiveness at customer touchpoints. Without consistent change across all touchpoints – concept, products, customer service, design – new brand value cannot be created. The key to success is focusing on essential value refinement rather than superficial makeovers.
Summary
Rebranding is an extremely important management strategy that redefines existing assets such as corporate history and strengths, creating new value adapted to changing times. For success, it’s essential to deeply analyze the current situation following the steps introduced in this article and thoroughly implement internal penetration (inner branding), not just external communication. Additionally, an attitude of carefully communicating the intent of change is required to avoid leaving existing customers behind. Organizational milestones and growth stagnation are also opportunities to significantly evolve the brand. Through rebranding that examines essential value, enhance corporate competitiveness and achieve sustainable growth.
Successful rebranding requires specialized knowledge from market analysis to brand strategy reconstruction and effective communication design. SUNNY SIDE UP leverages extensive PR and marketing experience to comprehensively support corporate brand value enhancement. If you have concerns about your company’s rebranding strategy, please first contact us through our inquiry form.
Inquiries | PR Company | SUNNY SIDE UP Inc.














